Best free password manager? Yeah, that’s a thing! Seriously, navigating the digital world without a solid password manager is like walking around with your wallet wide open. This isn’t just about remembering a bunch of crazy strings of characters; it’s about protecting your online life – your banking info, your social media, your embarrassing cat videos (we’ve all got ’em).
Table of Contents
We’ll dive into the best free options, comparing features, security, and ease of use, so you can find the perfect digital vault for your precious data.
Choosing the right free password manager is crucial for keeping your online accounts secure. This guide will help you navigate the options, examining factors like security protocols, platform compatibility, and user-friendliness. We’ll explore the pros and cons of various free services, helping you make an informed decision that aligns with your tech skills and security needs. Get ready to level up your digital security game without breaking the bank!
Top Features of Free Password Managers
Choosing a password manager can feel like navigating a minefield, especially when you’re trying to stick to a budget. Luckily, several excellent free options exist, each offering a compelling blend of features and security. However, understanding their strengths and limitations is key to making the right choice. This section compares and contrasts the core features of five leading free password managers to help you decide which one best suits your needs.
Free Password Manager Feature Comparison
The following table summarizes the core features, security protocols, and platform compatibility of five popular free password managers. Remember that features and security protocols can change, so always check the latest information on the provider’s website.
| Manager Name | Feature Set | Security Protocols | Platform Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitwarden | Password generation, storage, autofill, secure notes, shared folders (limited in free version), two-factor authentication (2FA) | AES-256 encryption, end-to-end encryption, zero-knowledge architecture | Web, Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, browser extensions |
| Dashlane (Free Version) | Password generation, storage, autofill, limited number of devices, basic security alerts | AES-256 encryption | Web, Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, browser extensions |
| KeePassXC | Password generation, storage, autofill, advanced features through plugins, open-source | AES, ChaCha20, Argon2 encryption (depending on configuration) | Windows, macOS, Linux, various mobile platforms via plugins |
| LastPass (Free Version) | Password generation, storage, autofill, shared folders (limited in free version), limited device support | AES-256 encryption | Web, Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, browser extensions |
| RememBear | Password generation, storage, autofill, relatively simple interface focused on ease of use | AES-256 encryption | Web, Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, browser extensions |
Limitations of Free vs. Paid Versions
Free password manager versions typically offer a core set of features, but paid subscriptions unlock more advanced functionalities. For example, free plans often limit the number of devices you can use, the amount of data you can store (like secure notes), and the number of shared folders or users. Paid versions usually offer family plans, priority customer support, and more advanced security features like dark web monitoring.
Think of it like this: the free version is a great entry-level tool, but the paid version is like upgrading to a premium car with extra features and safety systems.
User Experience Differences
The user experience varies significantly across different free password managers. Some, like RememBear, prioritize a minimalist and intuitive interface, making them ideal for users who prefer simplicity. Others, such as KeePassXC, offer a more customizable and feature-rich experience, but might have a steeper learning curve. Bitwarden strikes a balance, providing a robust feature set with a relatively user-friendly interface.
Dashlane and LastPass also offer user-friendly interfaces but have limitations in their free versions. Ultimately, the best user experience depends on individual preferences and technical skills.
Security and Privacy Considerations: Best Free Password Manager
Using a free password manager offers convenience, but it’s crucial to understand the security trade-offs involved. While they provide a significant improvement over writing down passwords, free services often rely on different security models and resource allocations compared to paid options, impacting the level of protection afforded to your sensitive data. This section will delve into the security implications of using free password managers, examining their encryption and storage practices, potential vulnerabilities, and the security certifications they might (or might not) possess.Free password managers typically employ encryption to protect your passwords.
However, the type of encryption, the key management practices, and where the data is stored significantly impact the overall security. Strong encryption, like AES-256, is a good sign, but the security of the system hinges on more than just the encryption algorithm. For example, a robust system would utilize end-to-end encryption, meaning only the user possesses the decryption key, and the provider cannot access your passwords even if compromised.
Conversely, a weaker system might store encryption keys in a less secure manner, creating a single point of failure. The location of data storage (e.g., servers in countries with varying data protection laws) also influences the security posture.
Data Encryption and Storage Practices
Free password managers vary considerably in their encryption and storage methods. Some might use strong encryption algorithms like AES-256, but the implementation details are crucial. For instance, one manager might use a zero-knowledge architecture where the provider doesn’t have access to your master password or decrypted data, while another might store data in a way that requires access to a decryption key held by the provider.
This key difference significantly affects the level of security. The physical location of servers where data is stored is also important; servers located in jurisdictions with less stringent data protection laws could expose your data to greater risk. Understanding these differences is key to selecting a secure option.
Potential Vulnerabilities
Free password managers, like any software, are susceptible to vulnerabilities. These could include software bugs allowing attackers to gain unauthorized access, weak server security leading to data breaches, or vulnerabilities in the authentication process. Additionally, phishing attacks targeting users could trick them into revealing their master password, compromising the entire system. A company’s security practices, including regular security audits and penetration testing, play a critical role in mitigating these risks.
A lack of transparency regarding security practices should raise concerns.
Security Certifications and Audits
The presence (or absence) of security certifications and independent audits is a crucial indicator of a password manager’s commitment to security. While not all free password managers undergo rigorous audits, those that do often undergo penetration testing and security assessments by third-party organizations. These audits verify the security of the system and identify potential weaknesses. Look for mentions of certifications like ISO 27001 (information security management) or SOC 2 (security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy).
The availability of such information demonstrates a commitment to transparency and security best practices. A lack of publicly available information regarding security audits should be a significant red flag.
Ease of Use and User Interface

Choosing a password manager shouldn’t feel like cracking a code itself. A good free option should be intuitive and easy to navigate, regardless of your tech skills. A clunky interface can quickly negate the security benefits, leaving you frustrated and less likely to use it consistently. This section explores the user interface aspects of free password managers, highlighting both excellent and less-than-stellar examples.
The user experience of a password manager hinges on seamless integration into your digital life. It needs to be simple enough for your grandma to use (no offense, grandmas!), but robust enough to handle the complex security needs of a cybersecurity professional. Think of it like this: a password manager should be a helpful assistant, not a demanding taskmaster.
User Interface Flowchart
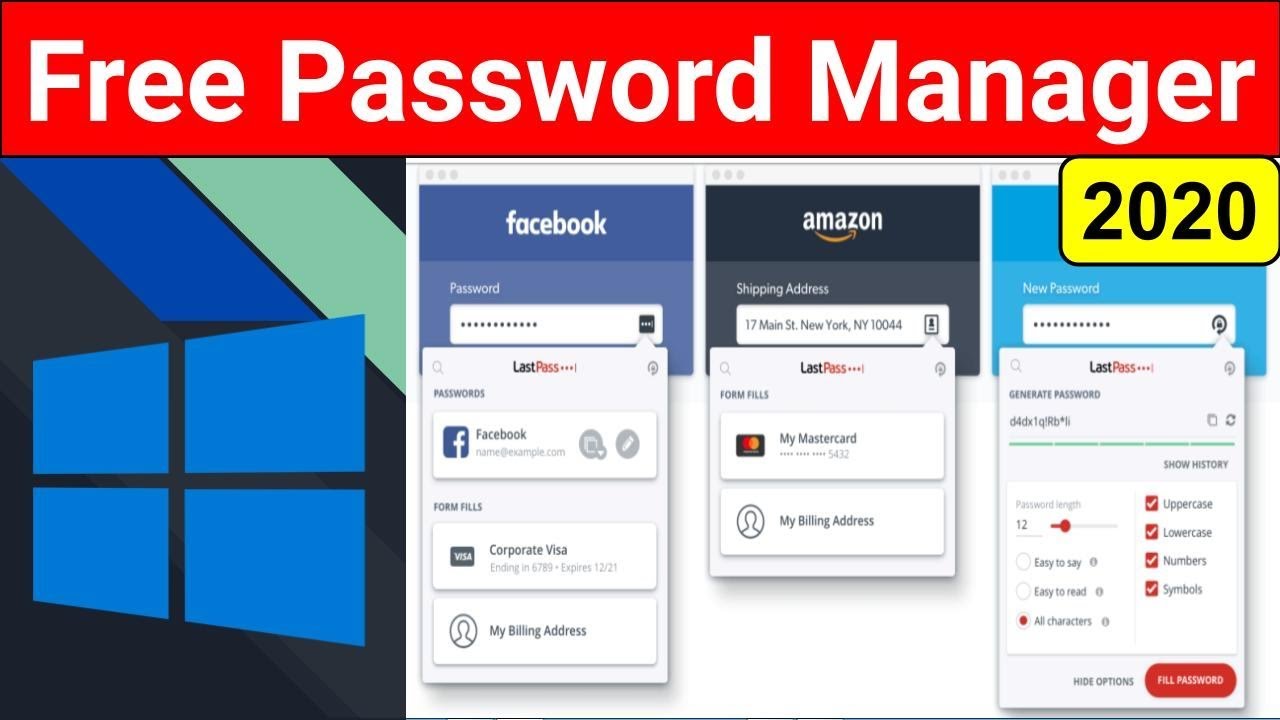
A typical user experience with a free password manager might look something like this (imagine a flowchart here): The user starts by creating an account, then installs the browser extension and/or mobile app. They then add their first website login, either manually or by importing from a CSV file. The manager autofills login credentials when visiting saved websites.
The user can then edit or delete entries as needed, and may choose to generate strong, unique passwords for new accounts. Finally, they can access their password vault securely using their master password or biometric authentication. The process should be fluid and require minimal clicks or steps. This simplicity is key to encouraging consistent use and maximizing the security benefits.
Examples of Intuitive and Unintuitive User Interfaces
Some free password managers, like Bitwarden, are praised for their clean, uncluttered interfaces. Their dashboard presents essential information clearly, making it easy to find what you need. The password generation feature is straightforward, and the autofill functionality works seamlessly across multiple browsers and devices. On the other hand, some less user-friendly options might present overwhelming amounts of information, have confusing navigation menus, or lack clear visual cues for important actions.
Imagine a password manager with a cluttered dashboard, nested menus, and cryptic icons – that’s a recipe for user frustration and ultimately, security risks.
Factors Contributing to Ease of Use, Best free password manager
Several factors contribute to a password manager’s overall ease of use. A well-designed interface is just the beginning; consider these additional aspects for a truly user-friendly experience.
- Intuitive Navigation: Clear menus, easily accessible settings, and logical organization of features are crucial.
- Seamless Autofill: The autofill feature should work reliably and unobtrusively across various websites and browsers.
- Simple Password Generation: The process of creating new, strong passwords should be quick and straightforward, ideally with customization options for length and character types.
- Secure Sharing Features: The ability to securely share passwords with others, if needed, should be easy to use and understand.
- Robust Mobile App Functionality: A well-designed mobile app is essential for convenient access to passwords on the go. The app should mirror the desktop experience in terms of functionality and ease of use. Features like biometric authentication (fingerprint or facial recognition) add extra convenience and security.
- Excellent Customer Support: Comprehensive and readily accessible help documentation and customer support can make all the difference when encountering issues.
Platform Compatibility and Device Support
Choosing a password manager often comes down to how well it integrates into your digital life. A manager that’s not compatible with your devices or preferred browsers is essentially useless, leaving your passwords vulnerable. This section explores the platform compatibility of popular free password managers and the implications of limited support.Platform compatibility refers to the range of operating systems (like Windows, macOS, iOS, Android) and web browsers (like Chrome, Firefox, Safari) a password manager supports.
Broad compatibility ensures seamless password management across all your devices and browsing environments. Limited compatibility, however, can force you to use different password management methods on different devices, increasing the risk of security breaches and decreasing convenience.
Operating System and Browser Support for Selected Free Password Managers
The following table shows the operating system and browser support for five popular free password managers. Note that support can change, so always check the password manager’s official website for the most up-to-date information.
| Password Manager | Windows | macOS | iOS | Android | Chrome | Firefox | Safari | Edge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bitwarden | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| KeePassXC | Yes | Yes | Yes (via third-party app) | Yes (via third-party app) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| LastPass (Free Version) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Dashlane (Free Version) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Zoho Vault (Free Version) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Implications of Limited Platform Compatibility
Limited platform compatibility significantly impacts user experience and security. For example, if a password manager only supports Windows and Chrome, a user primarily using a Mac and Firefox would be unable to seamlessly manage their passwords across all their devices and browsers. This might lead them to use different methods for different devices, increasing the risk of using weak passwords or writing them down.
Inconsistent password management practices significantly weaken overall security. A user might also need to switch to a different password manager altogether, potentially losing their existing data and workflow.
Setting Up and Synchronizing a Password Manager Across Multiple Devices
The process of setting up and synchronizing a password manager varies slightly depending on the specific application, but the general steps are similar. Let’s take Bitwarden as an example. First, you create a Bitwarden account on their website. Next, you download and install the Bitwarden app or browser extension on each of your devices (phone, laptop, tablet). After logging in with your Bitwarden credentials on each device, your password vault will synchronize across all platforms.
This allows you to access your passwords from anywhere, ensuring consistent security practices across your digital landscape. The synchronization process usually happens automatically in the background, but some password managers allow you to manually trigger it. Remember to always use a strong, unique master password to protect your password vault.
Import and Export Capabilities

Moving your passwords between password managers or backing them up is a crucial aspect of managing your digital life. Understanding how to import and export your data safely and efficiently is key to maintaining control and security. Different password managers offer varying levels of support for different data formats, and understanding these differences is important for choosing the right tool for your needs.Importing existing passwords into a new password manager can seem daunting, but most managers streamline the process.
Generally, the methods involve importing from a CSV file (Comma Separated Values), a common format used by spreadsheets and many applications, or directly from another password manager’s proprietary format if supported. Exporting, on the other hand, allows you to create a backup of your passwords, but it necessitates careful consideration of security to avoid unauthorized access.
Methods for Importing Passwords
The process of importing passwords usually involves navigating to the settings or import section within the password manager’s interface. Most free password managers provide a clear and straightforward method for importing passwords. This often involves selecting a file containing your passwords (often a CSV file) or using a built-in import function designed to work with other password managers.
Some managers may also support importing passwords directly from a browser’s password manager. For example, Bitwarden allows direct import from Chrome’s password manager, simplifying the transition for users switching services. Others might require exporting from the source manager to a CSV or a text file before importing into the new one. The level of user-friendliness varies, with some offering more intuitive interfaces than others.
Password Export and Security Considerations
Exporting your passwords from a free password manager is a necessary step for backup and migration, but it requires extra caution. The exported file contains all your sensitive data, making it a prime target for malicious actors. Therefore, it’s crucial to store the exported file securely, ideally using strong encryption and password protection. Keep in mind that the exported file is only as secure as the methods used to protect it.
Many password managers will allow you to export your passwords in a variety of formats, often including CSV and JSON, but these are often unencrypted. Some password managers might offer an encrypted export option, but this is not always standard across all free options. The best practice is to use a strong, unique password to protect the exported file and store it in a secure location, such as an encrypted cloud storage service or a physical drive secured with encryption.
Comparison of Data Formats
Different password managers support different data formats for import and export. CSV (Comma Separated Values) is a widely used, readily accessible format that most password managers support. It’s a simple text-based format, easily readable by spreadsheets and other applications. However, it usually doesn’t offer any encryption, so exporting in this format requires additional security measures. JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is another common format; it’s more structured than CSV, making it easier to parse programmatically but also requires extra security measures if not inherently encrypted by the password manager.
Some password managers might also support their own proprietary formats, which offer a seamless transition within their ecosystem but limit interoperability with other services. Choosing a password manager that supports common, open formats like CSV provides greater flexibility and reduces vendor lock-in. Encrypted formats, when available, should be preferred to protect your data.
Customer Support and Community Resources
Choosing a password manager often comes down to more than just features; reliable support is crucial, especially when dealing with something as sensitive as your online security. A robust support system can mean the difference between a frustrating experience and peace of mind. Let’s examine how different free password managers handle customer support and the role of community resources.This section will explore the various customer support channels offered by several popular free password managers, highlighting both positive and negative experiences reported by users.
We’ll also discuss the value of community-driven support forums and their impact on troubleshooting and problem-solving.
Available Customer Support Channels
Free password managers typically offer support through a combination of methods. Bitwarden, for instance, provides a comprehensive knowledge base with FAQs, detailed documentation, and video tutorials. They also offer email support for more complex issues and have an active community forum where users can help each other. LastPass, on the other hand, relies heavily on its knowledge base and community forums, with email support reserved for premium users.
Dashlane’s support structure is similar, although they may offer live chat for certain issues, but usually direct users to their extensive FAQ and help articles first. The availability and responsiveness of these channels can vary significantly.
Examples of Helpful and Unhelpful Customer Support Interactions
A helpful interaction might involve a prompt and thorough response to an email inquiry about a specific technical issue, leading to a clear resolution. For example, a user reporting a synchronization problem with Bitwarden might receive a detailed explanation of potential causes and troubleshooting steps, ultimately resolving the issue. Conversely, an unhelpful interaction might involve receiving a generic automated response to an email that doesn’t address the specific problem, leaving the user feeling frustrated and unsupported.
A user experiencing difficulty importing passwords into LastPass, for example, might receive a canned response directing them to the FAQ section without addressing the unique aspects of their import issue. The quality of support can vary greatly based on the specific manager and the complexity of the problem.
The Value of User Communities and Online Forums
User communities and online forums are invaluable resources for password manager users. These platforms provide a space for users to share their experiences, ask questions, and offer solutions to common problems. Bitwarden’s forum, for instance, is known for its active and helpful community, with users frequently assisting each other with troubleshooting and providing workarounds for various issues. The collective knowledge and experience within these communities often surpasses the resources available through official support channels.
Okay, so you’re looking for the best free password manager, right? Finding one that’s actually secure can feel like navigating a super complex project, almost like trying to implement agile methodologies in a chaotic startup. But once you find a solid option, managing all those passwords becomes way easier, freeing up your brainpower for more important stuff.
Seriously, a good password manager is a total game-changer.
Forums can be particularly useful for finding solutions to less common problems or for understanding best practices related to using the password manager effectively. However, it is important to remember that the information found in community forums is not always vetted and should be critically evaluated.
Password Generation and Strength
Choosing a strong password is crucial for online security, but remembering dozens of complex passwords is a nightmare. That’s where password managers come in, automating the process and ensuring your passwords are truly robust. They achieve this through sophisticated algorithms and user-friendly interfaces.Free password managers typically employ cryptographically secure pseudorandom number generators (CSPRNGs) to create passwords. These generators aren’t truly random (as that would require unpredictable physical phenomena), but they produce sequences that are statistically indistinguishable from random ones, making them incredibly difficult to predict.
They often combine this with character sets that include uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, resulting in passwords with high entropy – a measure of randomness. The specific algorithms used might vary between managers, but the core principle remains the same: generating unpredictable and complex character sequences. For example, a manager might use a combination of the Mersenne Twister algorithm (a widely used CSPRNG) and a carefully selected character set to build a password.
The length of the generated password is also a key factor, with longer passwords offering exponentially stronger protection.
Password Strength Indicators
Free password managers use different methods to visually represent password strength. Some use a simple color-coded system, with green indicating a strong password, yellow indicating a medium-strength password, and red indicating a weak password. Others provide a more detailed numerical score, showing a percentage representing the password’s estimated strength. Still others might offer a combination of both, providing both a visual cue and a numerical score.
The criteria used to determine password strength can also vary; some might prioritize password length, while others might place greater emphasis on the diversity of characters used. For instance, a password like “P@$$wOrd123” might receive a relatively low score in a manager that heavily penalizes easily guessable patterns, while a longer, more random password like “g7$hJ!p2kL9b&xR” would generally score much higher.
These variations in scoring systems mean that direct comparisons across different managers aren’t always straightforward, and users should focus on achieving the highest score possible within their chosen manager.
Password Change Recommendations and Features
Regular password changes are essential for maintaining security, especially in the event of a data breach. Free password managers often incorporate features to encourage this good practice. Some might offer a scheduled password change option, allowing users to set automatic updates for their passwords at regular intervals (e.g., every 90 days). Others might provide alerts or notifications when passwords are deemed too old or weak.
Many managers also offer bulk password changing capabilities, allowing users to update numerous passwords simultaneously, making the process less tedious. This is particularly helpful for users who manage a large number of online accounts. The frequency of recommended password changes is a subject of ongoing debate in the security community, with some arguing for more frequent changes and others suggesting that focusing on strong, unique passwords is more important than overly frequent updates.
The best approach is to follow the recommendations of your chosen password manager and to be vigilant about any suspicious activity on your accounts.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) Integration
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your password manager, making it significantly harder for unauthorized users to access your sensitive data, even if they somehow obtain your master password. Many free password managers offer 2FA integration, boosting their overall security profile. The specific methods and setup processes can vary, however.The integration of 2FA with free password managers generally involves linking your account to an external authentication method, such as an authenticator app or your email address.
This means that even if someone cracks your master password, they’ll still need access to your secondary authentication method to log in. This significantly reduces the risk of account compromise.
2FA Setup in Bitwarden
Bitwarden, a popular free and open-source password manager, offers 2FA via authenticator apps (like Authy or Google Authenticator) and security keys. Setting up 2FA in Bitwarden involves navigating to your account settings, selecting the “Two-Factor Authentication” option, and choosing your preferred method. If you opt for an authenticator app, Bitwarden will display a QR code that you scan with your app.
This will link your app to your Bitwarden account. After scanning the code, you’ll be prompted to enter a verification code from your authenticator app. Once confirmed, 2FA is enabled. For security keys, you’ll need to register the key through Bitwarden’s interface.
Comparison of 2FA Methods
Different free password managers support various 2FA methods, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Authenticator apps are widely available, user-friendly, and generally considered quite secure. They rely on time-based one-time passwords (TOTP), meaning the code changes frequently. Email-based 2FA is simpler to set up but can be less secure due to the vulnerability of email accounts to phishing attacks.
Security keys, like YubiKeys, offer the highest level of security as they are physically attached to the user. However, they require an additional hardware investment. The choice of method depends on your security needs and technical comfort level. A robust password manager should ideally support multiple methods to cater to diverse user preferences and security levels.
Browser Extension Functionality
Browser extensions are a game-changer for password managers, seamlessly integrating password management into your everyday browsing experience. They essentially act as a bridge between your password manager and your web browser, automating logins, securely storing credentials, and generally making your online life much less of a password-juggling headache. Without them, you’d be constantly copying and pasting, a practice ripe for security vulnerabilities.Browser extensions drastically improve the usability of password managers.
Instead of launching a separate application every time you need to log in, you can simply click an icon in your browser toolbar. This streamlined approach reduces friction and makes using a password manager far more convenient, thus encouraging consistent use – the key to strong password security. This convenience is a huge factor in why people actually
use* their password managers.
Security Risks Associated with Browser Extensions
Browser extensions, while incredibly convenient, introduce a layer of security risk. Because they have access to your browsing data, a compromised extension could potentially expose your login credentials or other sensitive information. This risk is magnified if you download extensions from untrusted sources or fail to keep your browser and extensions updated. Think of it like this: you wouldn’t leave your front door unlocked, and you shouldn’t leave your browser vulnerable to malicious extensions either.
Regularly reviewing your installed extensions and uninstalling those you no longer use is crucial for maintaining security. Reputable password manager companies rigorously vet their extensions, but vigilance is always advised.
Feature and Performance Comparison of Browser Extensions
Different password managers offer varying levels of functionality within their browser extensions. For example, some extensions might offer autofill for forms beyond just logins, including addresses and credit card details (though this adds another layer of security risk to consider). Others might provide enhanced security features like real-time phishing detection or warning you if you’re reusing passwords across multiple sites.
Performance can also vary, with some extensions consuming more system resources than others. A comparison might show that Bitwarden’s extension is known for its speed and lightweight design, while LastPass’s extension might offer more advanced features but potentially impact browser performance slightly more. Ultimately, the best extension for you will depend on your individual needs and priorities.
Open-Source vs. Proprietary Free Password Managers

Choosing between an open-source and a proprietary free password manager involves weighing different priorities. Open-source software offers a level of transparency and community scrutiny that proprietary software may lack, while proprietary options often provide more streamlined user experiences and dedicated support. Ultimately, the best choice depends on your individual needs and comfort level with technology.The core difference lies in the accessibility of the source code.
Open-source projects make their code publicly available, allowing anyone to examine, modify, and contribute to the software. Proprietary software, conversely, keeps its code private, limiting access and control to the developers. This fundamental distinction has significant implications for security, transparency, and user experience.
Transparency and Security Implications
Open-source password managers benefit from a community-driven approach to security. Multiple individuals can review the code, identifying potential vulnerabilities and contributing to fixes. This “many eyes” principle can lead to more robust security. However, this also means that the burden of security verification falls on the user; they must trust the community’s review process and the integrity of the codebase.
A less transparent, proprietary model, on the other hand, relies on the developer’s internal security practices and testing. While this can be effective, the lack of public scrutiny means potential vulnerabilities might go undetected for longer periods. The trust is placed solely in the company’s expertise and ethical conduct.
Examples of Open-Source and Proprietary Free Password Managers
Several examples illustrate the contrast. Bitwarden is a popular example of a proprietary password manager that offers a free tier with robust features. Its security relies on the company’s internal security audits and practices. In contrast, KeePassXC is a well-regarded open-source option. Its security is bolstered by the ability of the community to review and contribute to its codebase.
The user has more direct insight into the software’s inner workings, but also bears more responsibility for verifying its security. Another example of an open-source option is Password Safe, a more mature project that’s been around for a while and has a dedicated community.
Epilogue
So, finding the best free password manager for
-you* really boils down to finding the right balance between security features, ease of use, and platform compatibility. Don’t settle for a weak link in your digital armor! Take the time to explore the options, read reviews, and choose a manager that fits your needs and makes you feel confident about your online security.
Your future self (and your cat videos) will thank you.
FAQ Compilation
What happens if a free password manager goes out of business?
That’s a valid concern. If the service shuts down, you’ll lose access to your passwords unless you’ve exported them beforehand. Always back up your data!
Are free password managers less secure than paid ones?
Not necessarily. Many free managers offer robust security features, but they might have limitations on things like the number of devices you can sync or the level of customer support offered.
Can I use a free password manager for business purposes?
It depends on the specific manager and its terms of service. Some free options may have restrictions on commercial use. Check the fine print!
How do I know if a free password manager is trustworthy?
Look for transparency in their security practices, independent security audits, and strong encryption methods. Read reviews and check online security forums for feedback.
What if I forget my master password?
This is a disaster scenario! Most password managers don’t have a “reset” option. Choose a strong master password you can remember, and consider writing it down securely (if you’re comfortable with that).
